上 the manor system in feudal society map 114336-The manor system in feudal society map
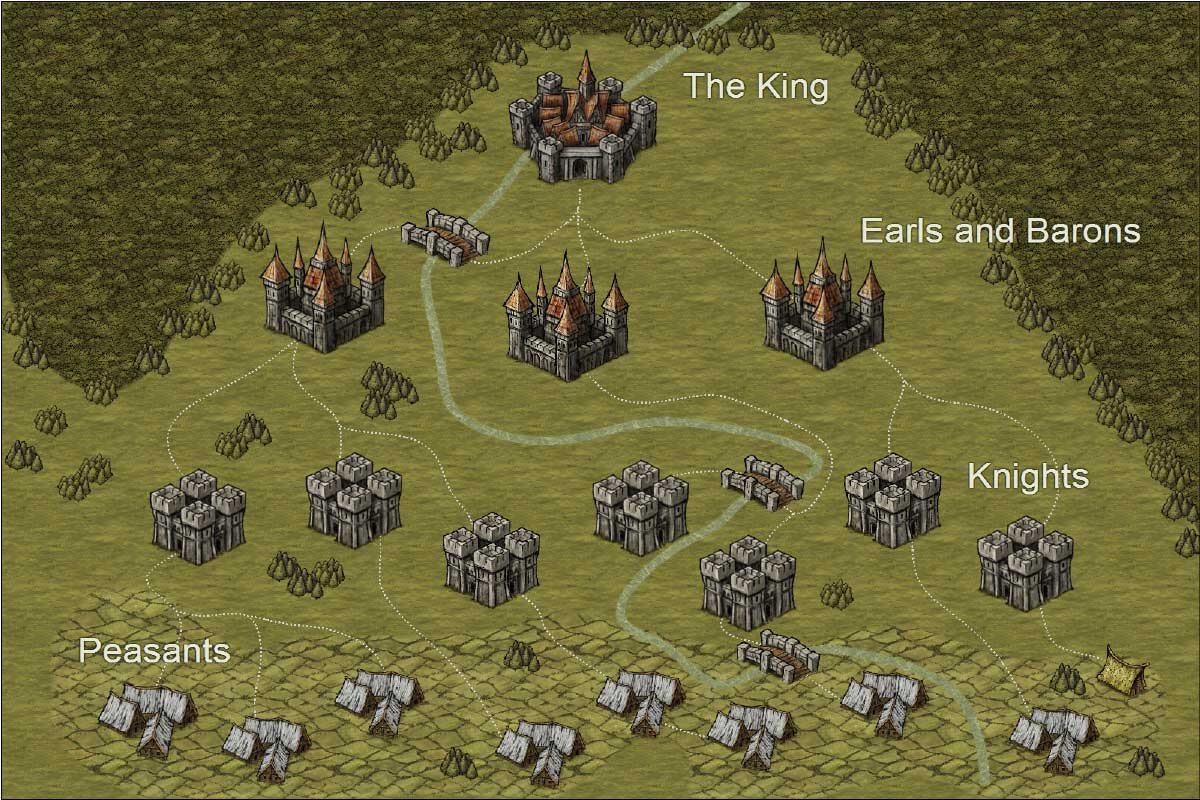
Feudalism, also known as the feudal system, was a combination of the legal, economic, military, and cultural customs that flourished in Medieval Europe between the 9th and 15th centuries Broadly defined, it was a way of structuring society around relationships that were derived from the holding of land in exchange for service or laborManors Support Feudalism • The heart of the feudal economy was the manor, or lord's estate • Most manors included one or more villages and the surrounding lands • Peasants, who made up the majority of the population in medieval society, lived and worked on the manorThis system of protection for provision was called the manorial system The manor was the lowest building block in the pyramid of the feudal system At the very top was the king The local manors were at the very bottom The local lord or noble was pledged to protect his village
The Manor System Life In The Middle Ages
The manor system in feudal society map
The manor system in feudal society map-Chapter 5 Europe in the Middle Ages Section 1 Feudalism and the Manor System Slideshare uses cookies to improve functionality and performance, and to provide you with relevant advertising If you continue browsing the site, you agree to the use of cookies on this websiteFeudal society & The manor System Feudal society by karthik gattepalliFeudal means to be decentralized;



Peasants Manors And Courts In The Middle Ages Medieval Society And The Manor Court Edited By Zvi Razi And Richard Smith Oxford Clarendon Press 1996 Pp Xiii 709 5 Maps
Manors Support Feudalism • The heart of the feudal economy was the manor, or lord's estate • Most manors included one or more villages and the surrounding lands • Peasants, who made up the majority of the population in medieval society, lived and worked on the manorThere are many resources available for teaching students about the feudal system of Medieval Europe, but there are very few about the complimentary manor system This product helps students understand the selfsufficient nature of medieval manors Contents * The Manor System Description (2 pageApart from it being the framework of society for centuries, a knowledge of the feudal system can be useful in genealogy when seeking to find the locations of even the smallest plots of land because (until 1812) the riveli (land tax rolls) often indicated such locations only by the manor (fief) where they were located
Feudalism & Medieval Life The Feudal System was introduced to England following the invasion and conquest of the island by William the Conqueror The Feudal System had been used in France by the Normans from the time they first settled there around 900 AD It was a simple, but effective system for the control of society by the King All land was owned by the King, and one quarter was kept byManor System Manor The estate of a knight or noble on a ʻfiefʼ of land Each manor was designed in the same basic way The management of the resources on the manor and its economy came to be known as the ʻManor SystemʼThe Feudal System Page 1, 2 The Feudal System information pages Page 3 Suggested Activities Page 4, 5 Feudal System Card Sort Page 6 Feudal System wordsearch Page 7 Feudal System true or false Section 2 the Manor and even had to ask for permission before they could marry
In the kingdom of England, a feudal barony or barony by tenure was the highest degree of feudal land tenure, namely per baroniam (Latin for "by barony"), under which the landholder owed the service of being one of the king's baronsThe duties owed by and the privileges granted to feudal barons are not exactly defined, but they involved the duty of providing soldiers to the royal feudal armyThe feudal system began a decline after Portuguese merchant sailors visited Japan and established trade relationships in 1542 The development of commerce and cities, and pressure from the West to trade with Japan, changed the environment in which the shoguns and daimyo ruledFEUDAL SOCIETY Kings and Queens Greatest lords of Europe All nobles and knights were their vessels How do you think most serfs felt about the manor system?



Standard 7 33 Lesson Ck 12 Foundation


Feudalism Was The Big Medieval Pyramid Scheme For The Soc
Pyramid) Lords provided land and protection while vassals provided money, advice, loyalty and military service 4 Define feudalism and manorialism Feudalism describes the relationship between the king and his nobles in mediaeval Europe Manorialism describes the relationship between a noble and his peasants in mediaeval Europe Feudalism was thus primarily political and military, whileFeudalism and manorialism (or manorial system) were the key characteristics of the Middle Ages Both terms refer to a landholding system in medieval Europe and were closely related, however, they were two distinct systems with several important differences The most important difference between feudalism and manorialism was their conceptFeudalism vs Manorialism Feudalism and Manorialism are two systems of thought that showed some difference between them in terms of the concept and understanding Manorial system concentrated on the organization of agricultural and craft production On the other hand, feudalism describes the legal obligation of vassal to nobles



Manorialism Definition Characteristics Britannica


Q Tbn And9gcs4 Cd5wxye Suxl8u6fnjv1 Wyozhg3qzx1glyx Gwpe8wdxqp Usqp Cau
Manorialism, also known as seignorialism or the manorial system, was an organising principle of rural economies which vested legal and economic power in a lord of the manorIf the core of feudalism is defined as a set of legal and military relationships among nobles, manorialism extended this system to the legal and economic relationships between nobles and peasantsThe manor system was a way that feudal lords organized their lands in order to produce agricultural goods The manor had four main areas the manor house and accompanying village, farmland,Manorialism, also known as the Manorial System, may be defined as the system in Medieval Europe where rural society was arranged around a manor house or castle on an estate The smallest units of these estates were also called manors Within the estates, free and unfree labourers (serfs or villeins) worked the land of the landowner (or its tenant) in return for protection and the right to work



Medieval Village Anatomy 101 My Literary Quest Medieval Medieval History History


Module 19 Google Slides
Find local businesses, view maps and get driving directions in Google Maps When you have eliminated the JavaScript , whatever remains must be an empty page Enable JavaScript to see Google MapsA manor house is a country house, which historically formed the administrative centre of a manor, the lowest unit of territorial organization in the feudal system in Europe A manor house was the dwelling house or "capital messuage" of a feudal lord of a manorPEASANTS AND MANOR LIFE The heart of the medieval economy was the manor, or lord's estate Most manors include one or more villages and the surrounding lands Peasants, who made up the majority of the population in medieval society, lived and worked on the manor Eleanor of Aquitaine Eleanor of Aquitaine married King Louis
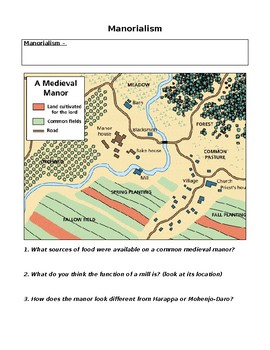


Manor System Manorialism Reading With Questions By Specedsoc Master



The Manor Life The Town Life The Manor Life In Medieval Europe More Than 90 Of The Population Lived In Rural Communities And Worked On The Land Ppt Download
The Manor System (Manorialism) was a key feature of society in the Middle Ages The Middle Ages (or Medieval Period) in Europe extended from approximately 500 CE after the fall of the Roman Empire to 1500 CE with the start of the RenaissanceThe Manor was based around a "Manor House" or castle where the noble/knight lives Fields were divided into three sections spring plantings, fall plantings, fallow field Peasants were given small strips of land to farm after working the lord's fields A mill ground grain, a church paid for by the noble was in the manorThe feudal system was a way of organising society into different groups based on their roles It had the king at the top with all of the control, and the peasants at the bottom doing all of the work


Www Wssd Org Cms Lib Pa Centricity Domain 575 Feudalism pp for study guide Pdf



Medieval Manor Map Medieval Medieval Life Medieval World
Feudal Society Sources DefinitionThe term feudalism refers to an economic, political, and social system that prevailed in Europe from about the ninth century to the fifteenth century With the chronic absence of effective centralized government during the Middle Ages, kings and local rulers granted land and provided protection to lesser nobles known as vassalsThe feudal system is a political system that was prevalent in Europe in between the eighth and fourteenth centuries Most of the agricultural societywas largely supported by the feudal system social hierarchyIn the feudal system, most of the rights and privileges were given to the Upper classesThe manor had its own court run by the lord or his steward In England, such a court, held in the great hall of a castle or manor, was known as a hallmote or halimoteDisputes between members of the manor estate on such things as the right to use particular areas of land like woodlands or peat lands (but not disputes between the lord and an individual peasant) were dealt with here, as well as



Medieval Farming Medieval Fields 3 Field Systems Picture Medieval Medieval Life Middle Ages



Manor European Society Britannica
Overview Feudalism was a set of legal and military customs in medieval Europe that flourished between the 9th and 15th centuries It can be broadly defined as a system for structuring society around relationships derived from the holding of land, known as a fiefdom or fief, in exchange for service or labourThe feudal system was a way of organising society into different groups based on their roles It had the king at the top with all of the control, and the peasants at the bottom doing all of the work652 Explain the effects of the Magna Carta on European society, its effect on the feudal system, and its contribution to the development of representative government in England 655 Summarize the origins and impact of the bubonic plague (Black Death) feudalism



Medieval Craft Minecraft Education Edition



Feudal Manor Worksheets Teaching Resources Teachers Pay Teachers
An overview of the Feudal Systemthe relationship of lords and vassals Titles of nobility such as dukes, earls, counts, viscounts and barons Homage and feThe feudal mode of production determined the social structure of feudal society (class stratification, hierarchy, the corporative system), society's political superstructure (public power as an attribute of landownership) and ideology (predominantly religious), and the sociopsychological makeup of the individual (communal consciousnessThe rise of feudalism in Medieval Europe greatly affected the social structure, specifically the rights and responsibilities of those who were in the noble and peasant class This rigid social structure, in turn, considerably impacted the society in different ways, ranging from the daily life of the people to the overall economy


Www Cabarrus K12 Nc Us Cms Lib Nc Centricity Domain 26 Life on a medieval manor pdf 2 Pdf



Manorialism World History Encyclopedia
Feudalism in Europe The First Feudal Age ( CE) Feudalism & Culture Life on a Manor Feudal Government (start with slide 8) The Early Middle Ages – The Feudal Spirit Feudal Society Feudalism in Europe Feudalism – The Fall of the Carolingians Feudalism and Life in the Middle Ages Feudalism and the Manor System Feudalism andThe manor system was used as a way of organizing agriculture and economic relationships between the lord and the peasant Peasants lived and worked on the manor which was owned by the lord The lord gave peasants protection and housing in exchange for their cropsFeudalism vs Manorialism Feudalism and Manorialism are two systems of thought that showed some difference between them in terms of the concept and understanding Manorial system concentrated on the organization of agricultural and craft production On the other hand, feudalism describes the legal obligation of vassal to nobles


Www Cabarrus K12 Nc Us Cms Lib Nc Centricity Domain 26 Life on a medieval manor pdf 2 Pdf


Early Middle Ages In Western Europe Feudalism 7th Grade S S
The feudal system is a political system that was prevalent in Europe in between the eighth and fourteenth centuries Most of the agricultural societywas largely supported by the feudal system social hierarchyIn the feudal system, most of the rights and privileges were given to the Upper classesThe system broke down in the later Middle Ages and feudal tenure was finally abolished in England, Ireland and Wales in 1660 The basic administrative unit was the manor Ideally a manor was enough land to support a cavalryman a knight's feeOverview Feudalism was a set of legal and military customs in medieval Europe that flourished between the 9th and 15th centuries It can be broadly defined as a system for structuring society around relationships derived from the holding of land, known as a fiefdom or fief, in exchange for service or labour


Www Cabarrus K12 Nc Us Cms Lib Nc Centricity Domain 26 Life on a medieval manor pdf 2 Pdf



Peasants Manors And Courts In The Middle Ages Medieval Society And The Manor Court Edited By Zvi Razi And Richard Smith Oxford Clarendon Press 1996 Pp Xiii 709 5 Maps
It was very difficult Social Studies 7th Map Quiz III Country/Capitol 7 Terms mrstorrescThere are many resources available for teaching students about the feudal system of Medieval Europe, but there are very few about the complimentary manor system This product helps students understand the selfsufficient nature of medieval manors Contents * The Manor System Description (2 pageEconomic system called manorialism, which centered around manorsThere were many key characteristics that defined the Medieval manorA manor was a large estate owned by a feudal lord, and the most common form of a fief (Ahlin 1, Nardo 19)Manors included a castle or manor house, at least one village, and the surrounding farmland (Frey 22) Manorialism was the name of the system that
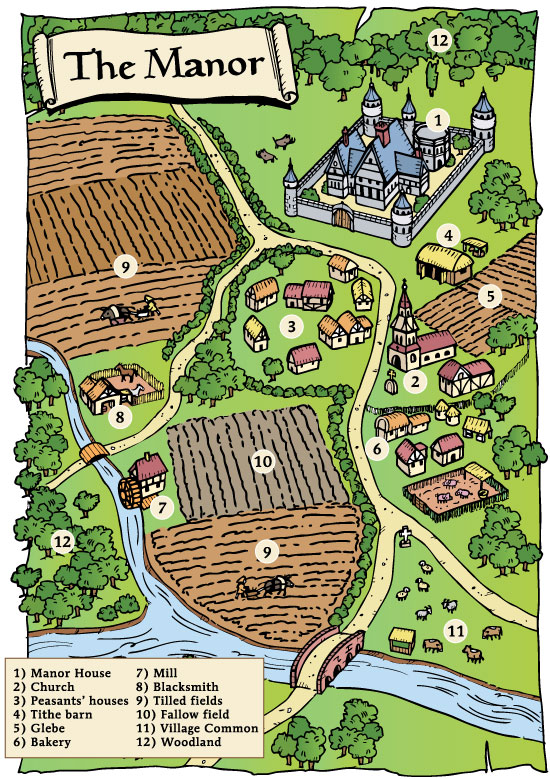


The Manor System
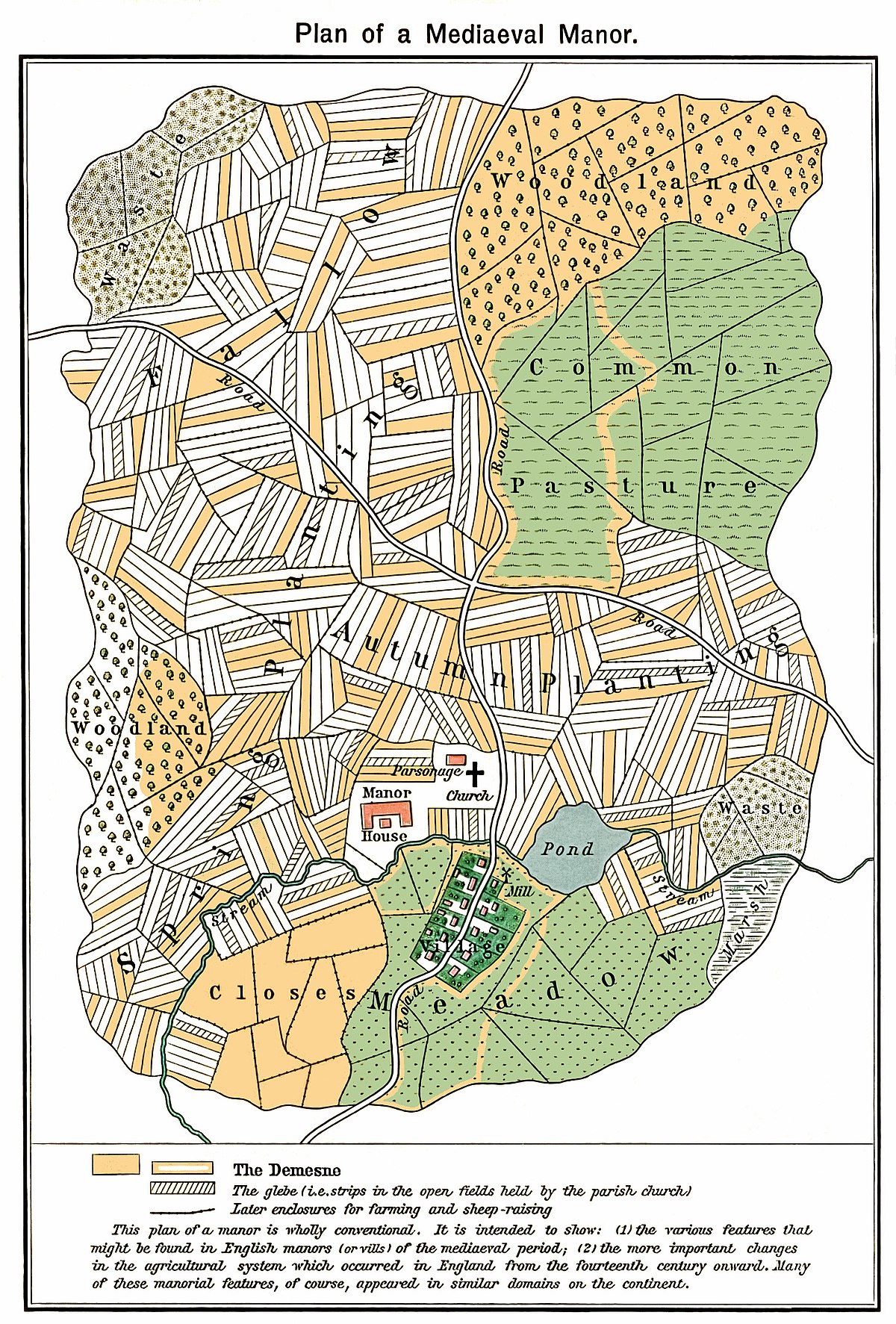


Manorialism Simple English Wikipedia The Free Encyclopedia
This video is about My MovieManorialism was an essential element of feudal society and was the organizing principle of rural economy that originated in the villa system of the Late Roman Empire Manorialism was widely practiced in medieval Western Europe and parts of central Europe, and was slowly replaced by the advent of a moneybased market economy and new forms ofFeudalism was a social order, and the manor system was the economic system During the feudal period in Europe, power & position in society were based on the Amount of land possessed The term feudalism is best defined as a System in which land is exchanged for military & loyalty



Medieval Manor System Page 1 Line 17qq Com


Economy Manorialism Medieval Worldview
How were feudalism and the manor system related?The Feudal System Under the feudal system all land in a kingdom belonged to the king He parcelled out large chunks to great Lords ("TennantsinChief") in exchange for their military and political support They parcelled out smaller parcels to lesser lords ("Mesne Tenants") on similar termsFeudalism Unit Castle Builder Fun activity where students design their castle blueprint and then attack each other The Feudal System (teachers) Feudal System unit One hour, simulating life in a feudal society, classroom activity Feudalism in Medieval Europe Lesson Plans Feudalism Resources (activity, working in small groups)



Feudalism Lesson For Kids Definition Facts Video Lesson Transcript Study Com



Serfs And Manorialism Video Khan Academy
No public authority, and responsibility, NO centralized governmentLocal territories get there own power of controlCounts took responsibility of local ter ritories, they took taxes and administration affairs, and military usesThis video is about My MovieIn an ideal feudal society (a legal fiction, most nearly realized in the Crusaders' Latin Kingdom of Jerusalem), the ownership of all land was vested in the king Beneath him was a hierarchy of nobles, the most important nobles holding land directly from the king, and the lesser from them, down to the seigneur who held a single manor


Clas Ucdenver Edu Nhdc Sites Default Files Attached Files Entry 147 Pdf



Feudalism 13 2 Dark Ages 13 1 Feudalism 13 2 A Church 13 3 France And England 13 4 Clash Over Germany Italy 13 5 Chapter Review In This Section You Will 1 Describe The Political Economic And Social Aspects Of Feudalism In Europe During The
Chapter 5 Europe in the Middle Ages Section 1 Feudalism and the Manor System Slideshare uses cookies to improve functionality and performance, and to provide you with relevant advertising If you continue browsing the site, you agree to the use of cookies on this websiteThe medieval manor, also known as vill from the Roman villa, was an agricultural estate During the Middle Ages, at least fourfifths of the population of England had no direct connection with towns Most people did not live on single farms as remains the case today, but instead, they were associated with a manor—a social and economic powerhouse of the Middle Ages



Manorialism Simple English Wikipedia The Free Encyclopedia



U11 L2 Feudalism Flashcards Quizlet



5 1 Feudalism And The Manor System


Medieval Europe Cities Religion And The Feudal System Brewminate
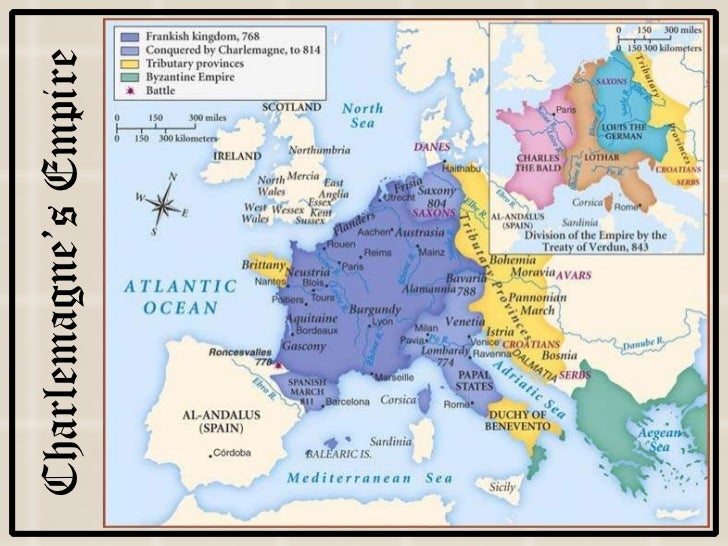


5 1 Feudalism And The Manor System



Lesson Plans



Medieval Manor System Page 1 Line 17qq Com



Manorialism Hbd Chick



Medieval Manor System Page 1 Line 17qq Com



A Plan Of A Typical Manor Village Medieval Medieval Life Middle Ages



The Feudal System Of Western Europe In Medieval Times


Q Tbn And9gctwm7izbqsp2uaeeojsljuc24s3bo32o V Z6lmu Rfnqoejydz Usqp Cau
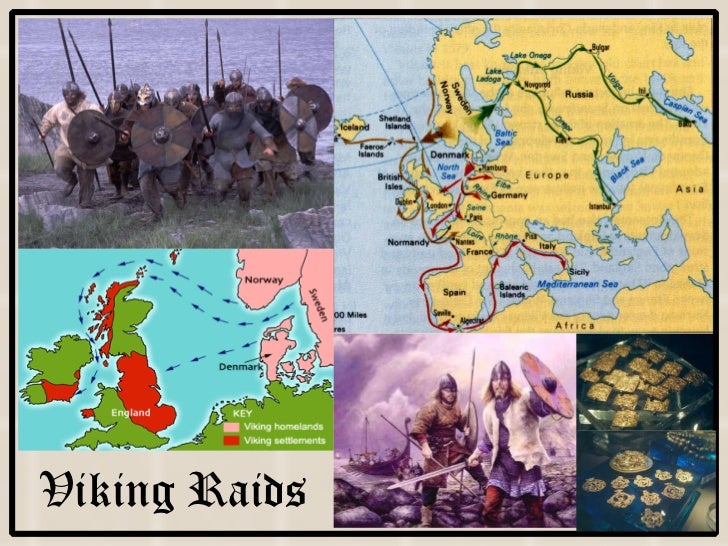


5 1 Feudalism And The Manor System



Family Feudalism


Www Decaturisd Us Cms Lib3 Tx Centricity Domain 3 Feudalism and chivalry lecture notes Pdf


The Manor System Life In The Middle Ages



Standard 7 33 Lesson Ck 12 Foundation



Middle Ages Manor House Drawing Burnsocial



Manor System Worksheets Teaching Resources Teachers Pay Teachers


Q Tbn And9gcqei41c Srjl4bhjgi Yrt8hdhbmx7tmcrkv8iw93xx1fqdaqqa Usqp Cau


Manor System The Middle Ages



Drainbamage Manor Of The Middle Ages Middle Ages Castle Parts Medieval Life



Lord Of The Manor Wikipedia


Http Www Swcta Net Teachers Brant World history Earlymiddle Ages Pdf



Diagram Of A Typical European Manor Circa 10 Mystery Of History Volume 2 Lesson 22 Mohii22 Medieval History Feudal System Medieval



5 1 Feudalism And The Manor System



Medieval Manor Map Serfdom Castle
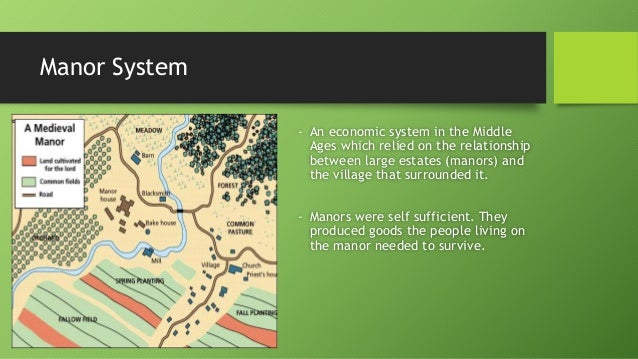


Middle Ages Feudal System



Bipartite Manorialism Hbd Chick


Q Tbn And9gcsocsz9o6anictqmoa Td2ezmnzxraiwj 9xykuz3mjocljynf6 Usqp Cau
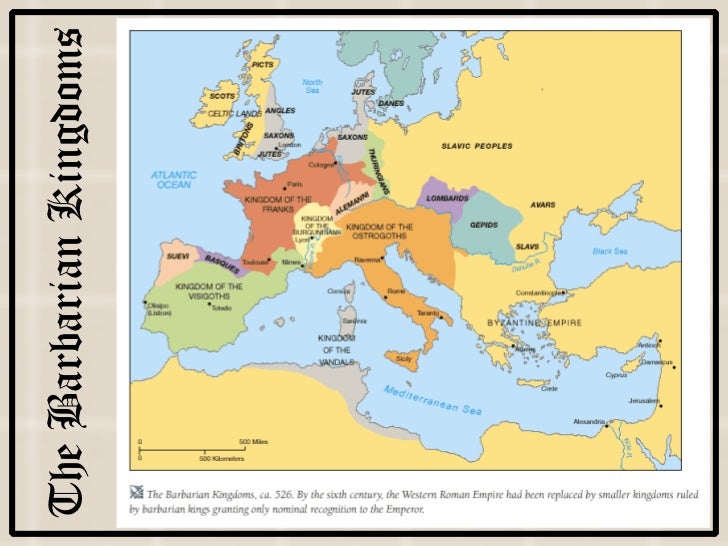


5 1 Feudalism And The Manor System



Section Ppt Download



Manorialism World History Encyclopedia


Europe After Fall Of Rome Mrs P Loves History And Avid


Digital Feudalism How The Data Ecosystem Is Becoming By Zach Scott Towards Data Science



Europe After The Fall Of Rome And Feudalism And The Manor System Ppt Download


Feudalism And Manorial System By Helee Patel



5 1 Feudalism And The Manor System


Medieval And Middle Ages History Timelines The Feudal System



Serf World History Encyclopedia
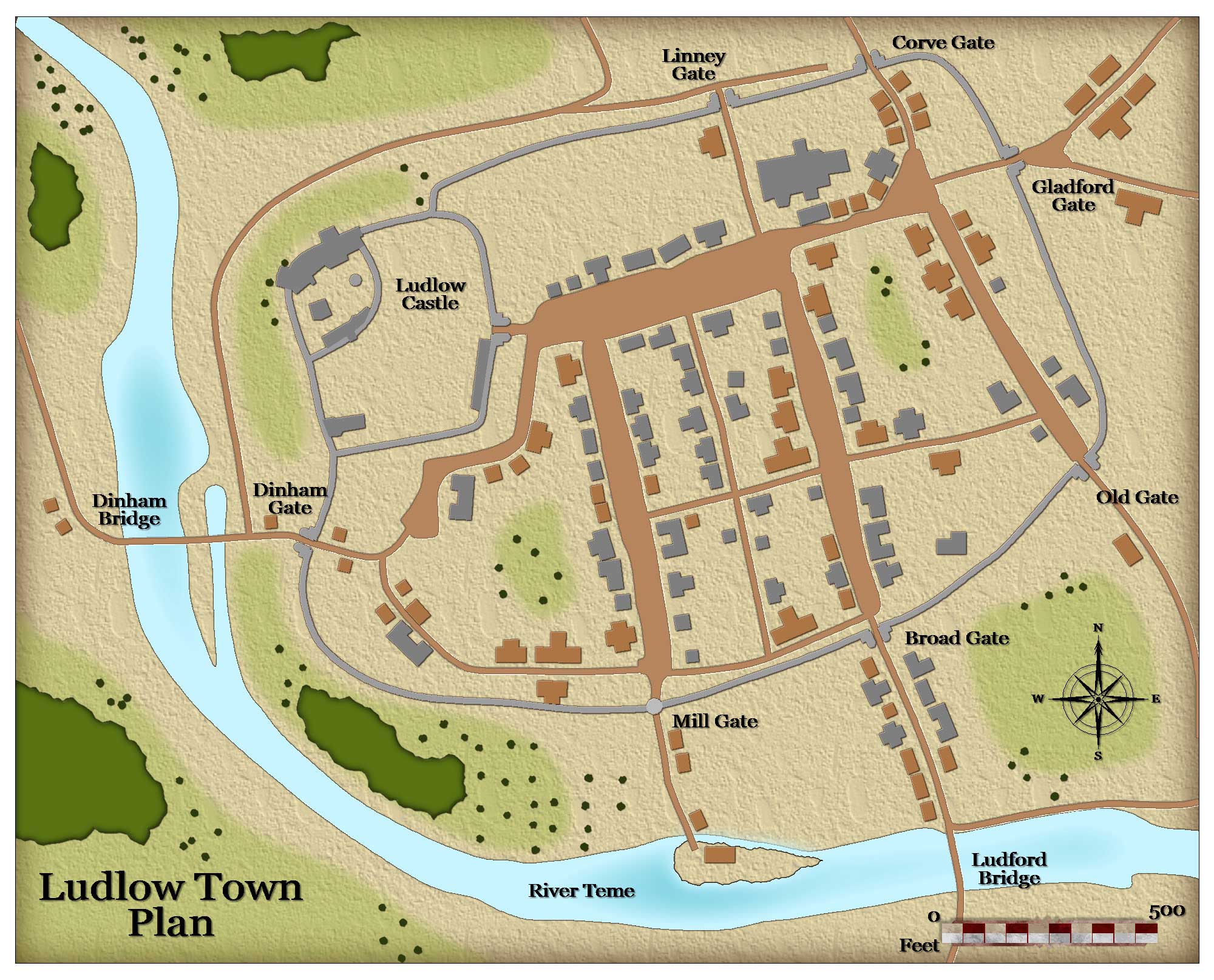


Medieval And Middle Ages History Timelines Medieval Ludlow



Manor System Worksheets Teaching Resources Teachers Pay Teachers


Medieval Technology And American History One Minute Essays Medieval Manors Vs Colonial Plantations



Medieval Manor Drawing Page 1 Line 17qq Com


Www Sps186 Org Downloads Basic Ch13 2 Pdf



Medieval Europe Medieval Medieval Life Medieval World



Medieval Europe Cities Religion And The Feudal System Brewminate



Serf Definition System Life Study Com



Manorialism Definition Characteristics Britannica



Feudalism Manor System Ppt Video Online Download



Western Europe In The Middle Ages Feudalism Offered Protection Land Owning Lords Gave Fiefs To Knights Who Swore To Protect Manor Political Organization Ppt Download



Serfdom Wikipedia



Life In A Manor Shoeing In Middle Ages



Pin By St John Vianney Catholic Scho On Sjvs 6th Grade Social Studies Education 6th Grade Social Studies 7th Grade Social Studies



The Manor System Western Civilization



The Manor Medieval England Medieval Medieval Life



Remix Of The Medieval Manor Assignment Thinglink Medieval Life Fantasy City Castle Layout


The Manor System Mr Gray S History Emporium



Get Medieval The Village In The Middle Ages Ludus Ludorum



The Feudal System Of Western Europe In Medieval Times


Norcoint Cnusd K12 Ca Us Userfiles Servers Server File Academics History social science Colangelo Chapter 9 the early middle ages Pdf



Medieval Manor And Village Circa 1100 Medieval Medieval Life Medieval Games



The End Of Feudalism Merchants And Mechanics


Norcoint Cnusd K12 Ca Us Userfiles Servers Server File Academics History social science Colangelo Chapter 9 the early middle ages Pdf


Economics Manor System Farming Feudal Society
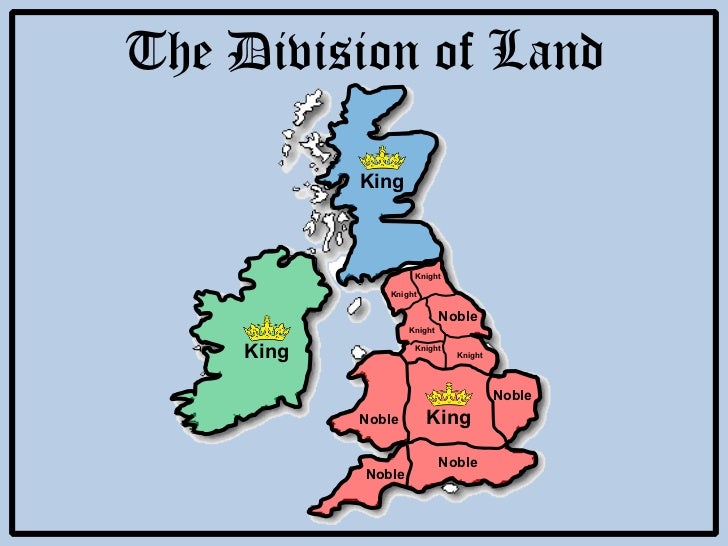


5 1 Feudalism And The Manor System


Http Windhamhs Ss12 Sharpschool Com Userfiles Servers Server File Feudalism In Europe Pdf



Manorialism World History Encyclopedia
/GettyImages-1053285684-96b37b776fea4dfe86631a23a0c23d5c.jpg)


What Is Manorialism


Plan Of A Medieval English Manor



Feudal Manor System Page 1 Line 17qq Com



Manorialism



Manorialism Definition Characteristics Britannica



5 2 11 Br Describe Why This Symbol Is Associated With A Feudal Society Today Life In The Middle Ages The Manor System Ppt Download



Medieval Manor System Page 5 Line 17qq Com
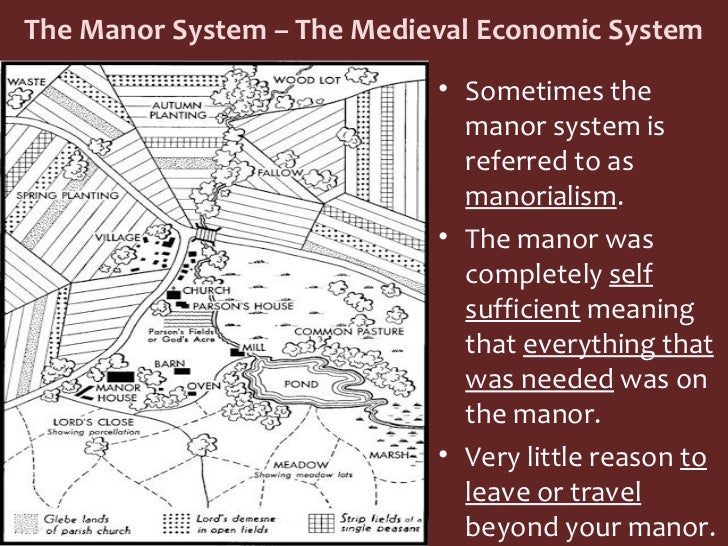


Middle Ages Feudalism And Manor Lesson Ppt


コメント
コメントを投稿